Abstract:
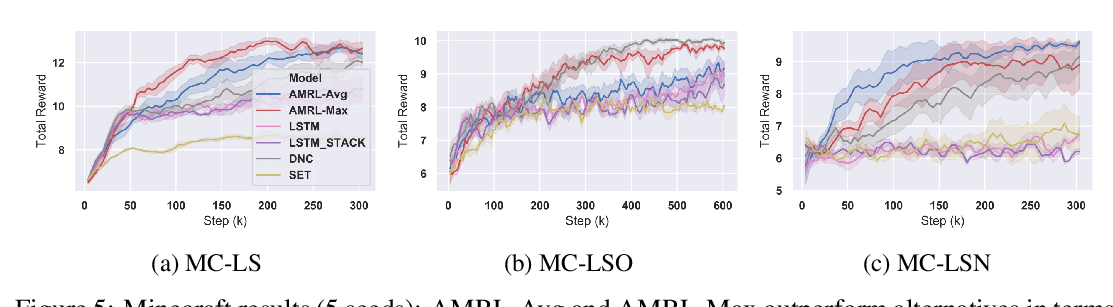
The practical usage of reinforcement learning agents is often bottlenecked by the duration of training time. To accelerate training, practitioners often turn to distributed reinforcement learning architectures to parallelize and accelerate the training process. However, modern methods for scalable reinforcement learning (RL) often tradeoff between the throughput of samples that an RL agent can learn from (sample throughput) and the quality of learning from each sample (sample efficiency). In these scalable RL architectures, as one increases sample throughput (i.e. increasing parallelization in IMPALA (Espeholt et al., 2018)), sample efficiency drops significantly. To address this, we propose a new distributed reinforcement learning algorithm, IMPACT. IMPACT extends PPO with three changes: a target network for stabilizing the surrogate objective, a circular buffer, and truncated importance sampling. In discrete action-space environments, we show that IMPACT attains higher reward and, simultaneously, achieves up to 30% decrease in training wall-time than that of IMPALA. For continuous control environments, IMPACT trains faster than existing scalable agents while preserving the sample efficiency of synchronous PPO.